If we compare DeFi trading to the handling of the One Ring, consider decentralized exchanges as the people Frodo (or, in this case, you) meets along the way. You’re processing a lot of information as you head towards Mordor, but not all of them will be giving you the right directions. Some will deceive.
Where Frodo has a sword, bow, and an ax supporting him, your journey towards filling your digital wallet will require mastery (or at least familiarity) of several DeFi trading tools. But Gandalf tells Frodo where to go, and without him, the Fellowship may not have succeeded. That’s what an oracle crypto does for your crypto transactions—the oracle is the Gandalf showing you the way.
Blockchain on its own requires a lot of external data to flow through it, which is where Oracles come in. Today, we’ll discuss what an oracle in the world of crypto is and take a look at some of the most popular oracle crypto projects that you should familiarize yourself with if you are getting into smart contracts.
Oracles in the Crypto World – An Overview
The efficiency of a blockchain is heavily dependent on the smart contracts that run on it. The number of transactions smart contracts can initiate increases with the volume of information they process, and ultimately, this will also lower the gas fees required per transaction.
To understand how much of a difference it makes, think of it as the difference between going to Mordor on foot versus flying in with eagles.

These smart contracts also reduce the transactional risks associated with traditional financial models, along with providing transparency. However, there is a very prominent issue that needs to be addressed. Otherwise, everyone would employ the best possible smart contract and call it a day, right?
Blockchains require a lot of external data to flow through them, and at the same time, this data is coming from an equally large number of sources. Providing this data requires a lot of processing power and data feeds, also known as Oracles.
There is a lot of debate going on around the topic of Oracle. Still, there is no denying that the current pace of expansion the blockchain system is seeing because of Oracle’s accurate data transferability.
For the orcs, the all-seeing eye is Sauron, while for the Fellowship, its’ Gandalf. For your digital currency ventures, it’s Oracle since every bit of external data flows through it. In cases where oracles represent third-party data feeds, several privacy and information issues may arise.
The biggest question here is how can oracles be trusted? Is it safe to trust new oracle crypto projects with sensitive information on the blockchain?
What Is an Oracle in Crypto?
Think of oracle cryptos as bridges that connect blockchains to the external world. These are third-party smart contracts that DEXs and currency operators often use to bridge the gap between on-chain and off-chain interaction for the blockchain.
Oracles become decentralized information networks, helping blockchains grow out of their data nests and interact with the real world.
You need to note that blockchains can interact with the external world without oracles, but you must enter the data manually. This slow, painstaking process carries a lot of risk for introducing error.
The way oracles work may seem fun from an employment point of view, but the biggest issue here would be introducing bias. The interaction procedure becomes faster and more accurate with oracles, giving the chain every opportunity to grow.
The name for these smart contracts couldn’t be more apt, considering how oracles used to be mystics giving people information they didn’t have access to otherwise.
Understanding Oracle Meaning Better – How It Works
Blockchains need real-world data to determine the price of a given currency, post transactions, give ownership, and more. Oracles take off-chain, real-world data and give it to the blockchain. The chain directs the oracle to where this data has to be placed.
Suppose you bet on whether or not Viggo Mortensen broke his toe during that scene (sorry, we had to). In that case, an oracle can search the entire internet for a reliable source of information, check whether he actually did break it or not, and then post the information on the chain.

The contract would then execute the transaction and disburse your winnings immediately.
This example shows that not only do oracles provide data to smart contracts, but they also issue commands required to execute a transaction. The data they provide is designed to be used with smart contracts, and oracles can also be programmed to do other tasks.
For example, it can confirm with each data stream sent over if the transaction has been completed or a price cap or bottom has been reached, and more. It can even be programmed to initiate a transaction if it rains in the real world!
The oracles crypto meaning suggests that the concept has limited use. In reality, they have become an essential part of the blockchain infrastructure, particularly smart contracts. The input they give is crucial for ensuring the legitimacy of contracts. However, there is a debate around the topic.
The Debate For & Against Oracles
Our current blockchain infrastructure suggests that oracle crypto projects are the figurative backbone of DeFi trading and dApps. However, at the same time, it is an all-seeing eye that gets access to crucial data, making blockchain’s privacy feature attractive. They represent a threat to the safety net that users hide behind.
That is not to say that the identity of persons initiating the transactions is laid out clearly in front of oracles. They will have to work quite a bit to identify users still; however, it’s possible nonetheless.
This is known as the Oracle Problem. Ensuring the trustworthiness and reliability of oracles is key to the successful implementation of a smart contract. While Oracles don’t have access to the funds of a cryptocurrency itself, they do have access to patterns and potentially identifiable information.
Because of the utility and value Oracles represent, getting rid of them isn’t a viable solution. However, the issue can’t be left unaddressed, either. Whether oracles represent the eye of Sauron or Gandalf’s staff is still a matter of debate.
Understanding The True Oracle Meaning
Blockchain can’t interact with external factors easily, making its privacy features and decentralized nature possible. Furthermore, there is a deterministic nature of every event and its direct or indirect impact on the price, and this requires that everything is posted in a logical order.
But when gathering said data, it may not be possible for the data to be sequential every time. Therefore, it would be impossible for the blockchain to understand and post. This ‘flow’ of data timeline is what gives blockchain its immutable characteristic. Blockchain cannot be altered in any way.
Oracles can analyze, record, and sort real-world events and turn them into a deterministic form that’s more compatible with blockchain infrastructure. Of course, different coins have slight variations in features and how they protect their data/users. Oracles must keep that in mind when processing data.
Oracles are essentially smart contracts themselves and, therefore, need to be updated with the blockchain continuously. It needs to find solutions for data collection, analysis, sorting, and posting on and off-chain.
Currently, Oracles are known for forming connections between blockchains and existing web APIs, allowing payments directly via web applications. Take the Kraken app, for instance – or any other DEX.
There are five types of Oracle crypto projects.
- Hardware: Hardware oracle crypto projects are designed specifically to interact with the physical world. These smart contracts keep an eye on external events on which certain transactions are contingent. Once the event happens, the transaction is executed with respect to the terms and conditions of, say, a bet.
- For example, the increasing oil price, real estate market fluctuations, insurance premiums, and more, all of these factors can be tracked by Oracle, and transaction(s) can be initiated once conditions are fulfilled.
- Software: Software oracles handle all the information collected or required by the smart contract, and in essence, the blockchain. Once the data is gathered, it will be transmitted to the blockchain with the web API. Because of the relative unreliability of information on the internet, the data is verified. Oracles can cryptographically attest the data’s origin via dedicated protocols, like TLSNotary, and push the attested data forward.
- For example, data collected can include asset prices, weather conditions, flight information, the value of a coin, and more.
- A prime example of a software oracle is Oraclize.
- Consensus Building: Consensus building is where a smart contract determines the authenticity of information collected, physically or online, based on how popular a decision is.
- For example, predictor markets used this oracle crypto project fairly often.
- Inbound Oracles. These are contingent oracles that rely on external scenarios, waiting for something to happen so that they can initiate a transaction. It is mostly used to trigger sells and buys based on a coin’s performance.
- Outbound Oracles. These are oracle crypto projects allowed to send the collected data to sources other than the blockchain network. It could be sending the data to other blockchains, software, or even other oracles.
IBM and Microsoft are some of the biggest information providers out there, offering a blend of software and hardware oracle solutions for enterprises and blockchains.
Oracle Crypto Projects List
Chainlink

Considered to be the leader in the oracle space, Chainlink brought the adoption of blockchain oracles into the light. It aims to ensure secure data inputs and outputs and has benefited quite extensively from being an industry pioneer. It managed to capture a rather large market share, partnering with Kyber, Opium Network, Synthetix, and more.
Chainlink is under scrutinized and centralized control because of its decentralized network’s governance protocols. Hence, it is transparent to some extent, but some aspects could still use improvement.
Many new oracle crypto projects threaten Chainlink’s position as the market leader because of several new technologies, features, and more transparent workflows.
At the time of writing, the Chainlink token (LNK) is valued at $32.02 with a market cap of ~$10.96 billion and geared for a 50% price increase as it partners with Associated Press for data.
Band Protocol

Unlike other oracle cryptos, Band Protocol works on Cosmos instead of Ethereum. This gives it access to a more robust system of blockchains to work with, and the company aims to take advantage of that. Band Protocol is pursuing the long-term goal of creating an ‘Internet of Blockchains.’
Its native token, BAND, saw a 9,000% growth in the value in the DeFi space in 2020 because of its interoperability and strong similarities to Chainlink. Band Protocol is much more interoperable in comparison to Chainlink.
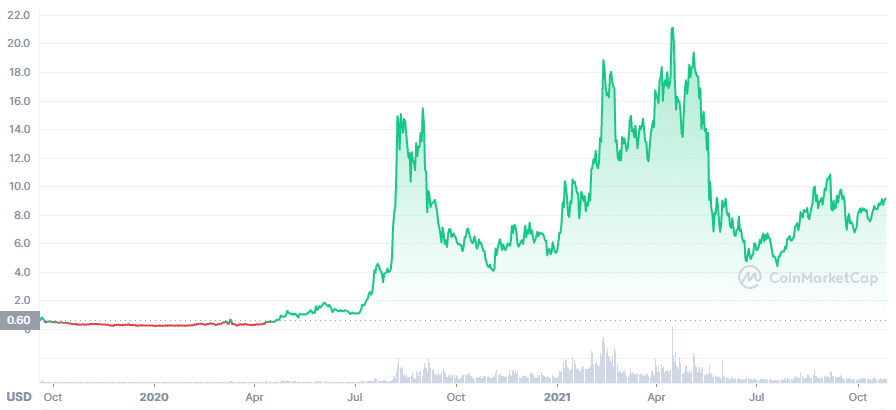
Furthermore, the adoption of Cosmos instead of the Ethereum Network is also crucial for bridging connections with other blockchains. However, Cosmos doesn’t allow such a robust and transparent governance as others, including Chainlink, which is a problem.
Band Protocol (BAND) is currently valued at $9.14, ranking at the 174th position. It has a market cap of $321 million only, showcasing its adolescence in the market.
Nest Protocol

Nest prides itself on being the first oracle network that produces and verifies price data on-chain. At the same time, its governance protocol (consensus mechanism) allows it to be completely transparent with its data collection, pricing, and calculation structure.
Despite being a new oracle project, it has managed to make a mark on its peers.
Because of its Chinese origins, the protocol may not seem as trustworthy at first. The English language support is a bit lacking at times, which doesn’t help build trust.
The NEST token is currently valued at $0.0121 with a trading volume of $1.8 billion and is ranked 779th on the list. However, it can easily capture a global market and go higher based on current trends and ongoing development (such as better translation).
Others
Other more successful oracle projects include:
- Tellor. One of the most ambitious projects on the list is more concerned with high-quality price feeds for decentralized applications. The network incentivizes other oracles to provide off-chain data with its native currency, Tributes (TRBT). Valued at $0.5867, the token ranks at 6179th position. It is at a much lower price point now compared to when it was launched in October 2020. It has also managed to get financial backing from several big currencies, such as Binance, Maker DAO, Consensus, and more.
- DIA Association. Made with data and for those who need diverse data, this is an oracle project made for DeFi platforms that don’t mind the extra external data. It is an open-source oracle platform that offers processed, decentralized
- data, and anyone can adopt it.
- Dos Network. The network is a data and power provider for the truly ambitious blockchains with a primary focus on computational power. The native Dos Network token (DOS) is valued at $0.02484 with a market cap of $3.3 billion – which can be diluted to ~$23.5 billion.
There are several other oracle crypto projects, each with a unique benefit and feature to offer. While some offer governance to dictate what the all-seeing eye sees, others aren’t as forthcoming. Here is a table to show how these networks compare.
| Oracle Project | Chain | Governance | Data Validation | Data Sources | Data Transparency |
| Chainlink | Ethereum | Centralized | Decentralized | Multiple | Limited |
| Brand Protocol | Cosmos | Decentralized | Decentralized | Multiple | Yes |
| Nest Protocol | Ethereum | Decentralized | Decentralized | Singular | Yes |
| Tellor | Ethereum | Decentralized | Decentralized | Singular | Limited |
| DIA | Ethereum | Decentralized | Decentralized | Multiple | Yes |
| Dos Network | Ethereum | Decentralized | Decentralized | Multiple | Limited |
Looking Into the All-Seeing Eye of Oracle Projects
The concept of Oracle Crypto has several benefits to boast, but there is also a concern for users. Then, there is the issue of oracle exploits. They aren’t as rare, but they can’t be classified as ‘uncommon’ either. As long as they perform as they should, it is sufficient to say that they are pretty. However, a closer look reveals an entirely different story.
For example, an oracle exploit in November 2020 saw $89 million being liquidated on Compound. After investigation, it was revealed that Compound was functioning as it should. However, we should not stop asking questions about the oracle’s integrity. In October 2021, $16 million were stolen from Indexed Finance, but whether the oracle was to blame or not is still unclear.
These risks are precisely why the debate about Oracle projects is still ongoing. What do you think about oracles? Are they safe? What improvement would you suggest to them? Or would you suggest that they are like the Mines of Moria, never to be ventured into?
If you’d like to read about more exploits or learn more about navigating the DeFi fields safely, we recommend going through our guide here.